Definition of Open Innovation
Open innovation can be defined based on the definition of innovation. According to Schumpeter (1934) innovation is defined as the successfull implementation of something new.
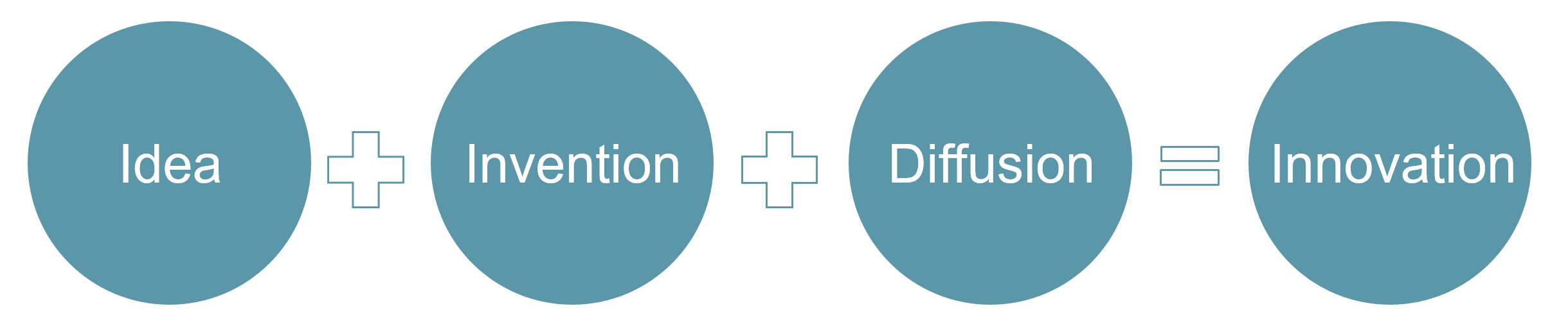
This definition implies the three elements of idea, implementation and diffusion:
An Idea (lit. mental image) is an incidence or a new thought before implementation. An archetype that has signification and attracts attention.
Invention is the act of turning imagination into a new product or service by solving objective technical problems in expectation of some improvement or advantage.
And the Diffusion, the process by which a new idea or new product is communicated through and accepted by the market or members of a social system.
Henry Chesbrough, in 2006 defined Open innovation as the use of purposive inflows and outflows of knowledge to accelerate internal innovation and expand the markets for external use of innovation, respectively.
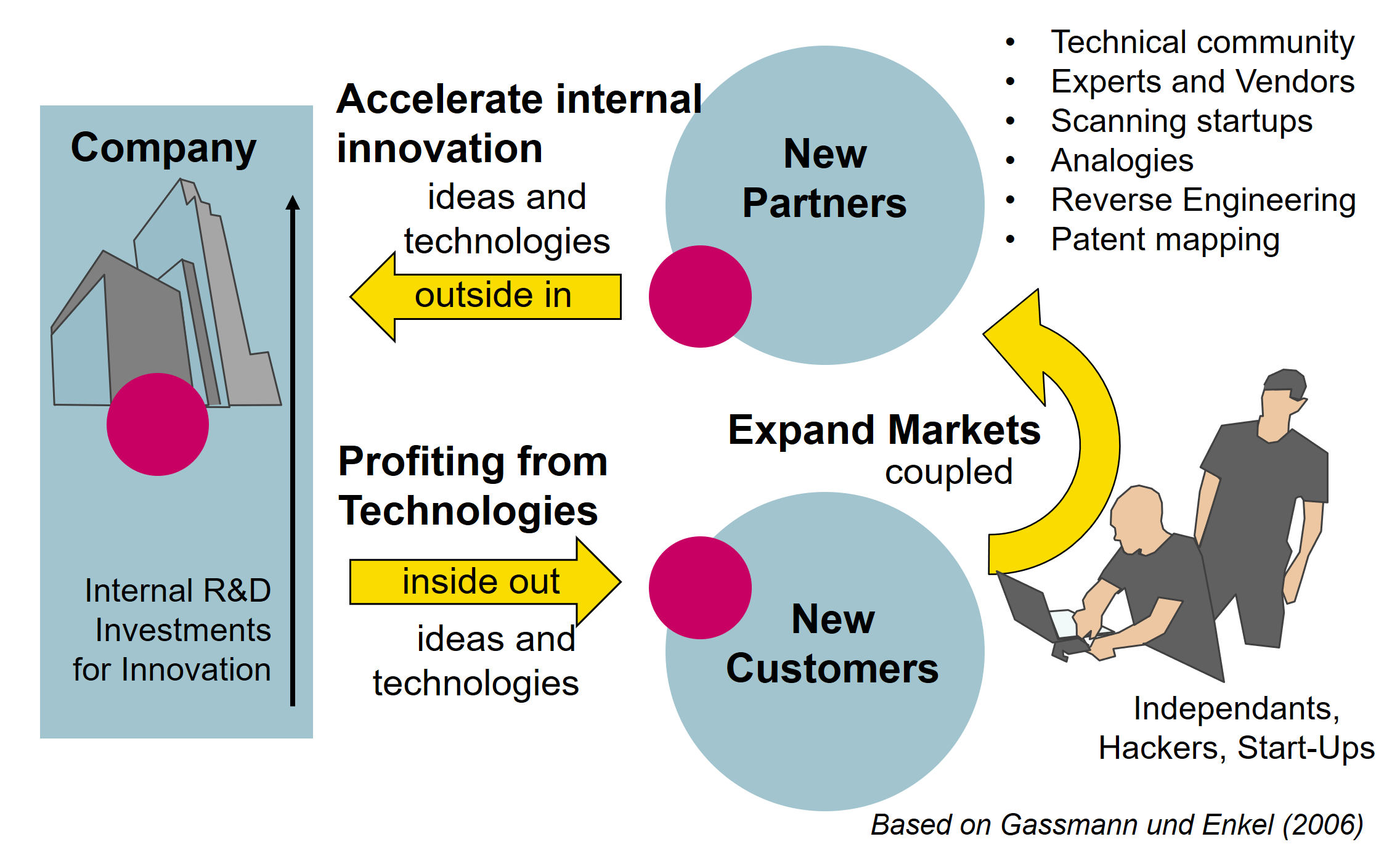
And later in 2014 as a distributed process based on purposively managed knowledge flows across organizational boundaries, using pecuniary and non-pecuniary mechanisms in line with the organizations business model.
Interestingly, Eric von Hippel uses the same term of Open Innovation to define am more democratized innovation. He states that Innovation is open when all information related to innovation is public good, nonreivalrous, nonexcludable. Also somethimes refered to as User Innovation, Free Innovation or Open Source Innovation.
Outside in: scouting, in-licensing IP, university research, funding startups, collaborating with intermediaries, customers, suppliers, non disclosure, crowdsourcing, competitions, communities, spin-ins, spin-backs
Inside-out: selling, revealing, out-license IP, technology, donating IP, spin-outs, corporate venture capital, corporate incubators, joint ventures alliances (becoming a supplier)
Coupled: joint venture, collaborative development, commercialization, consortia, networks, ecosystems, platforms, toolkits for user
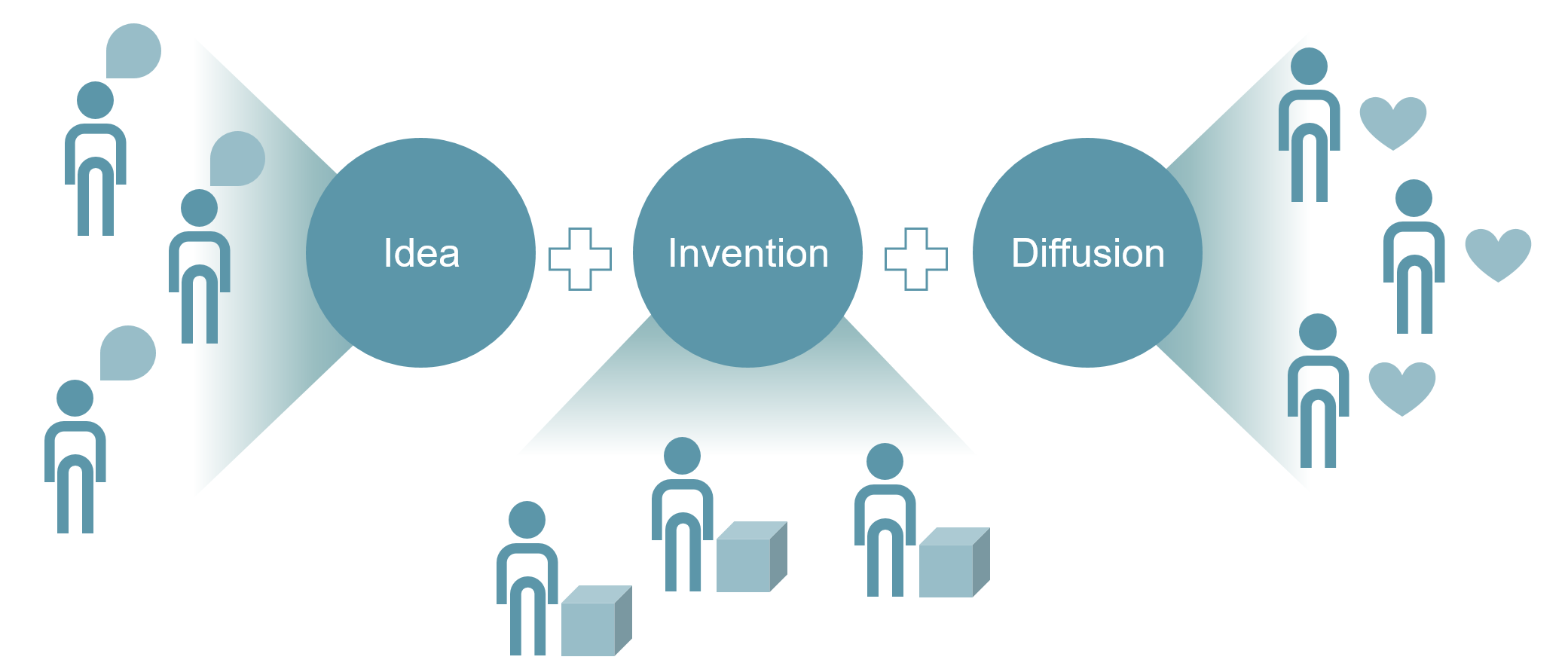
| Idea | Invention | Diffusion |
|---|---|---|
| – Systematic Ideation – Open Thinking – Crowdsourcing – Co-Creation – Voice of the Customer – Lead-User – Crowd funding – Crowdvoting |
– Partners, Experts and Vendors – Analogy / Competitor Analysis – Reverse Engineering – Technology Monitoring – Patent mapping – Technology Hypecycles – Technology Start-Ups – Co-Production / Co-Testing |
– Trend Research – Adoption Lifecycle – Business Eco-Systems – Communities of Practice – Trend-Scouting – Co-Launching |
Just as traditional innovation, open innovation can be managed in organizations. Innovation management is the systematic planning, implementation and control of innovation in organizations. In addition to the ideation, which deals with the development of ideas, innovation management also includes the implementation of ideas and their translation in commercially successful products and services.
Open Innovation is based on trustful cooperation – The Innovation Network
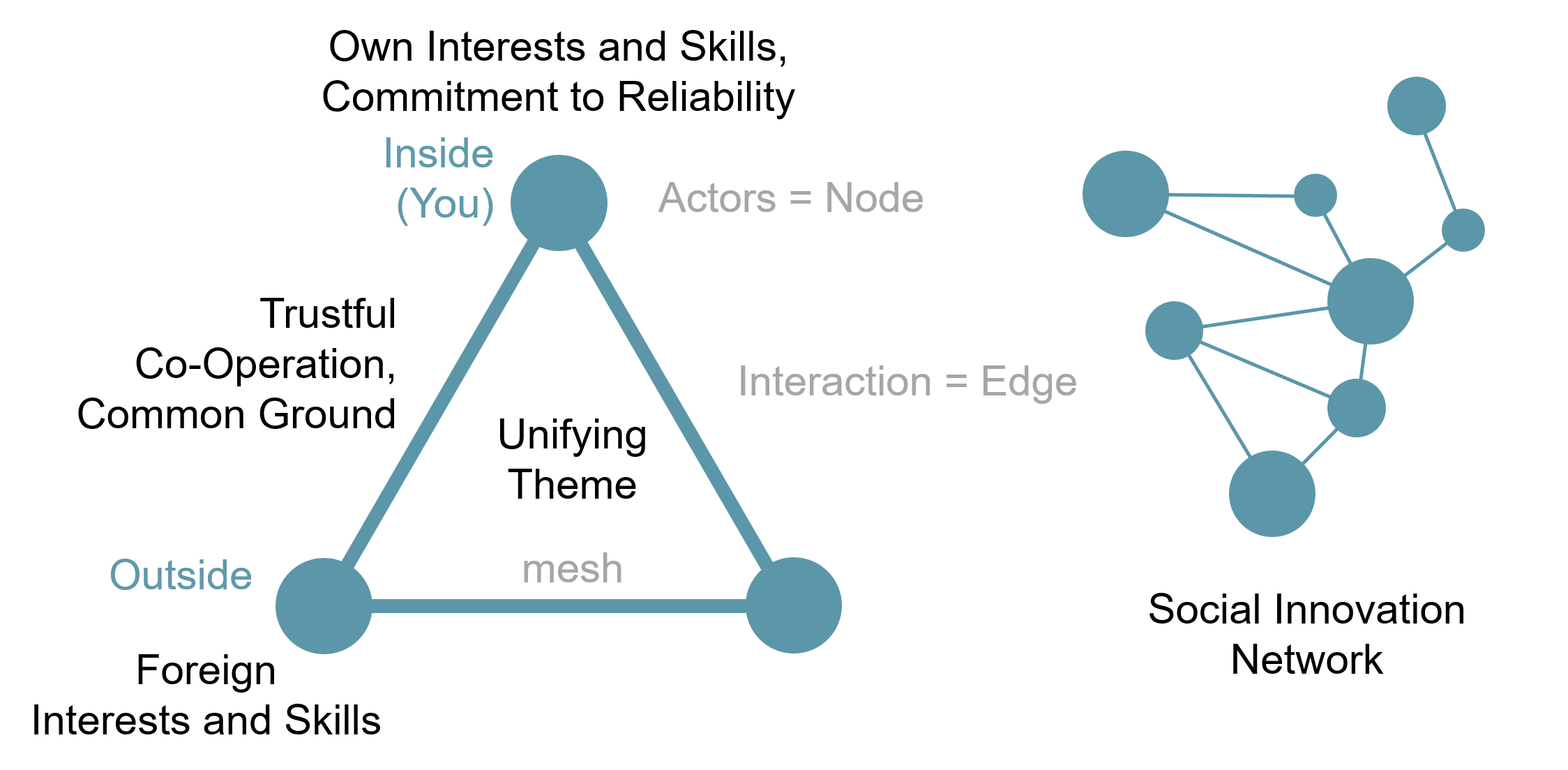
In addation, open innovation requires a social system, the patterned network of relationships constituting a coherent whole that exist between individuals, groups, and institutions. Wheras the network is defined by the interaction (edges) of individual actors (nodes). The benefits of the network is the optimization of resource use through exchange.
In business ecosystems economic communities of interacting organizations and individuals, producing goods and services, coevolve and align themselves.
